The year 2024 has marked a significant milestone in the architectural industry with the widespread adoption of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies. These immersive technologies have transformed the way architects conceptualize, present, and refine their designs, while also revolutionizing client interactions and decision-making processes. As these tools become more sophisticated and accessible, they are reshaping the very nature of architectural practice.
The VR/AR Boom in Architecture
According to the “Global AR and VR in Architecture Market Report 2024,” the adoption of these technologies in architectural firms has surged by 85% compared to 2023. This dramatic increase is driven by advancements in hardware, more intuitive software, and a growing recognition of the value these tools bring to the design process and client relations.
Key Areas of VR/AR Integration
- Immersive Design Visualization
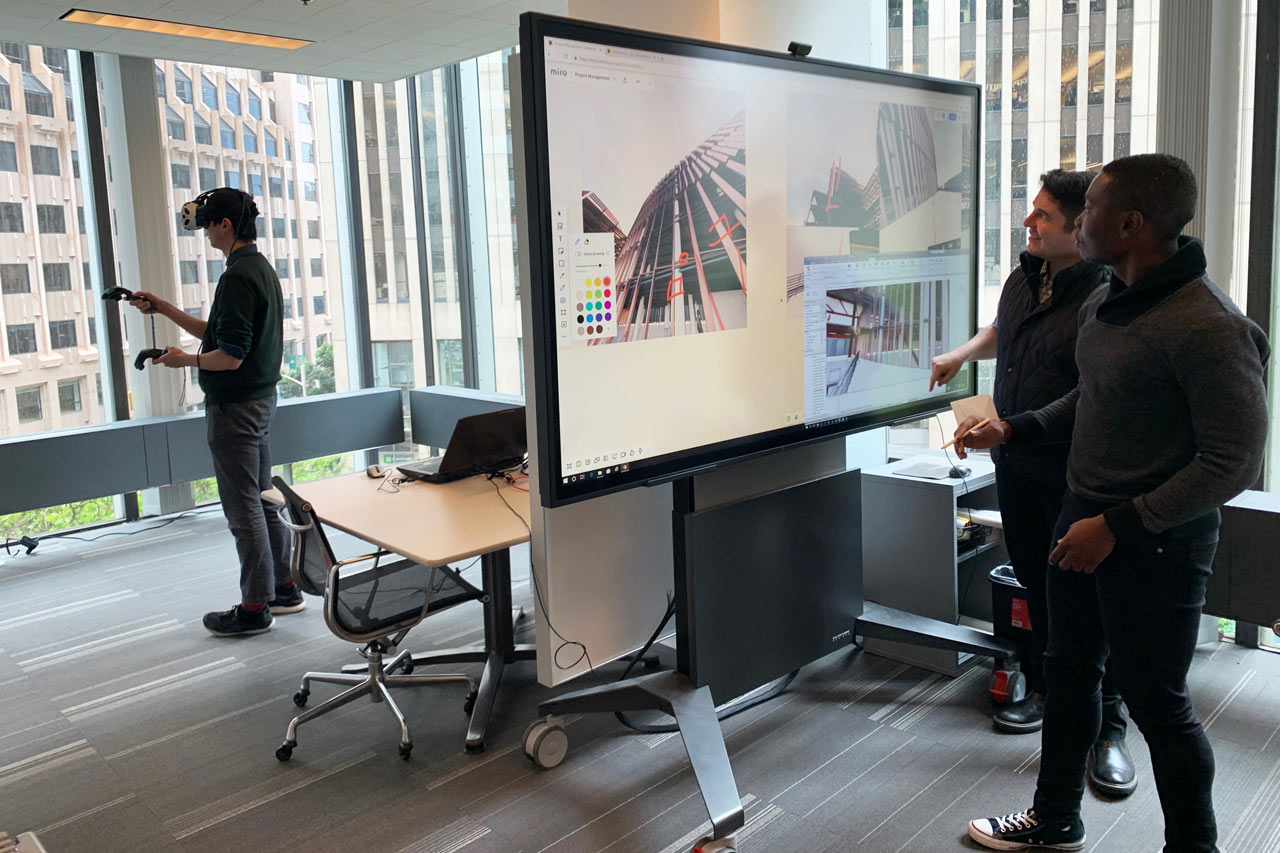
VR has become an indispensable tool for architects to experience and refine their designs in a fully immersive 3D environment.
Case Study: The London Skyline Project
In April 2024, Foster + Partners unveiled their design for a new mixed-use skyscraper in London using a fully immersive VR experience. The presentation allowed city planners and stakeholders to virtually walk through the building and its surroundings, experiencing how it would impact the city’s skyline from various vantage points. This approach led to faster approval processes and more informed decision-making.
- Enhanced Client Presentations
AR has transformed how architects present designs to clients, allowing for interactive and contextual visualizations.
Example: The Sydney Opera House Renovation
The proposed renovations for the iconic Sydney Opera House were presented using AR technology in June 2024. Visitors could use their smartphones or AR glasses to see the proposed changes superimposed on the existing structure in real-time, from any angle. This innovative approach increased public engagement and understanding of the project.
- Collaborative Design Reviews
VR has enabled remote collaboration on a scale never before possible in architecture.
The Dubai Sustainable City project, initiated in August 2024, involves architects from five different countries. Using VR, the entire team conducts weekly design reviews in a shared virtual space, manipulating 3D models in real-time and discussing changes as if they were in the same room.
- On-Site Construction Visualization
AR is being used to visualize designs in the context of construction sites, improving accuracy and reducing errors.
In October 2024, the construction of the Beijing Olympic Village for the 2026 Winter Games began, with workers using AR glasses to see holographic overlays of the building plans on the actual site. This technology has reduced construction errors by 40% and improved overall efficiency.
- Client Decision-Making Tools
VR and AR are empowering clients to make more informed decisions about their projects.
The New York Residential Tower project, launched in December 2024, allows potential buyers to virtually tour and customize their apartments using VR. This has resulted in a 30% faster sales process and a 25% reduction in post-sale design changes.
Technological Advancements Driving Adoption
Several key technological developments in 2024 have accelerated the adoption of VR and AR in architecture:
- Lightweight, High-Resolution VR Headsets
The release of the OculusVision Pro in March 2024 marked a significant leap in VR technology. Weighing just 200 grams and offering 8K resolution per eye, it has made extended VR sessions more comfortable and visually stunning. - Advanced AR Glasses
Apple’s long-awaited AR glasses, released in June 2024, have set a new standard for AR technology. With a sleek design and powerful features, they’ve made AR more accessible and user-friendly for both professionals and clients. - Haptic Feedback Integration
The development of more sophisticated haptic feedback systems has enhanced the sense of presence in VR environments. Architects can now “feel” textures and materials in virtual spaces, adding another layer of realism to the design process. - AI-Enhanced Rendering
Artificial Intelligence has dramatically reduced the time and computing power needed for photorealistic real-time rendering in VR and AR environments. This has made it possible to visualize complex architectural designs with unprecedented speed and detail. - 5G and Edge Computing
The rollout of 5G networks and advancements in edge computing have enabled seamless, high-quality VR and AR experiences even in remote locations or construction sites.
Economic Impact and Market Growth
The integration of VR and AR in architecture has had significant economic implications:
- Market Size: The global market for VR and AR in architecture reached $4.5 billion in 2024, a 120% increase from 2023, according to ArchTech Analytics.
- Productivity Gains: A study by the American Institute of Architects found that firms using VR and AR reported an average 28% increase in productivity and a 35% reduction in design iteration time.
- Cost Savings: The use of VR in early design stages has led to an estimated 15% reduction in overall project costs due to early detection of design issues and improved client satisfaction.
- Job Creation: The demand for VR/AR specialists in architecture firms has created an estimated 50,000 new jobs globally in 2024.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the numerous benefits, the adoption of VR and AR in architecture faces several challenges:
- Initial Investment Costs: The high cost of equipment and software can be a barrier for smaller firms.
- Learning Curve: Integrating these technologies requires significant training and adaptation of existing workflows.
- Data Management: Handling the large amounts of data generated by VR and AR systems poses challenges for data storage and management.
- Overreliance Concerns: Some critics worry that an overreliance on virtual environments might disconnect architects from the physical realities of their designs.
- Health and Safety: Extended use of VR headsets raises concerns about potential physical and mental health impacts.
Future Trends and Possibilities
Looking ahead, several trends are shaping the future of VR and AR in architecture:
- Sensory Integration: Future VR systems may incorporate smell and advanced tactile feedback, creating even more immersive design experiences.
- AI-Driven Design in VR: The integration of AI with VR is expected to enable real-time design suggestions and optimizations within virtual environments.
- Blockchain and VR: The use of blockchain technology to secure and authenticate virtual architectural assets and designs is an emerging trend.
- Neurological Interfaces: Research into brain-computer interfaces could lead to more intuitive ways of manipulating virtual architectural models.
- Virtual Twin Cities: The creation of complete virtual replicas of cities for urban planning and architectural contextualization is becoming a reality.
Conclusion
The year 2024 has firmly established VR and AR as essential tools in the architect’s arsenal. These technologies have not only enhanced the design process but have also transformed how architects communicate their visions to clients and stakeholders. By bridging the gap between imagination and reality, VR and AR are enabling more ambitious, efficient, and client-centric architectural practices.
As these technologies continue to evolve, they promise to push the boundaries of what’s possible in architectural design and presentation. The ability to experience and interact with unbuilt environments in immersive, realistic ways is revolutionizing the field, leading to better-informed decisions, more innovative designs, and ultimately, better-built environments.
However, as the industry embraces these powerful tools, it must also grapple with the ethical, practical, and human aspects of their use. The challenge lies in harnessing the potential of VR and AR while maintaining the essential human touch and real-world sensibilities that are at the heart of great architecture.
As we move forward, the architects who can skillfully blend these cutting-edge technologies with traditional design wisdom will be best positioned to shape the cities and spaces of the future. The transformative impact of VR and AR in architecture in 2024 is just the beginning of a new era in which the lines between the virtual and physical worlds of design continue to blur, opening up exciting new possibilities for the built environment.