Introduction
The concept of smart buildings, enhanced by the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT), represents a significant advancement in the field of architecture and urban planning. Smart buildings utilize technology to optimize the efficiency of building systems, improve the comfort and safety of occupants, and reduce environmental impact. As we move through 2022, the evolution of smart buildings and IoT continues to transform how we design, construct, and manage built environments. This article delves into the key features, benefits, and future trends of smart buildings, highlighting the role of IoT in shaping the future of architecture.
Understanding Smart Buildings and IoT
Definitions and Key Components
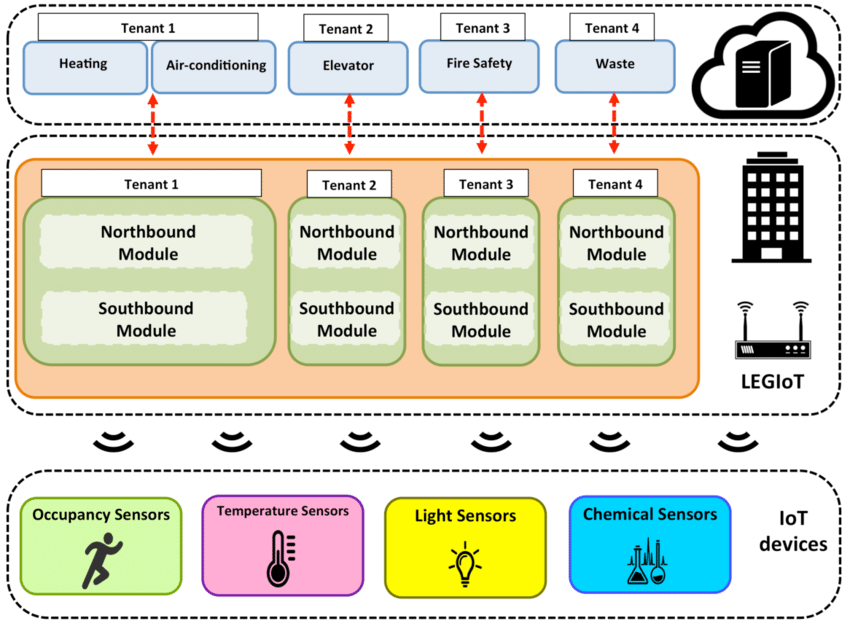
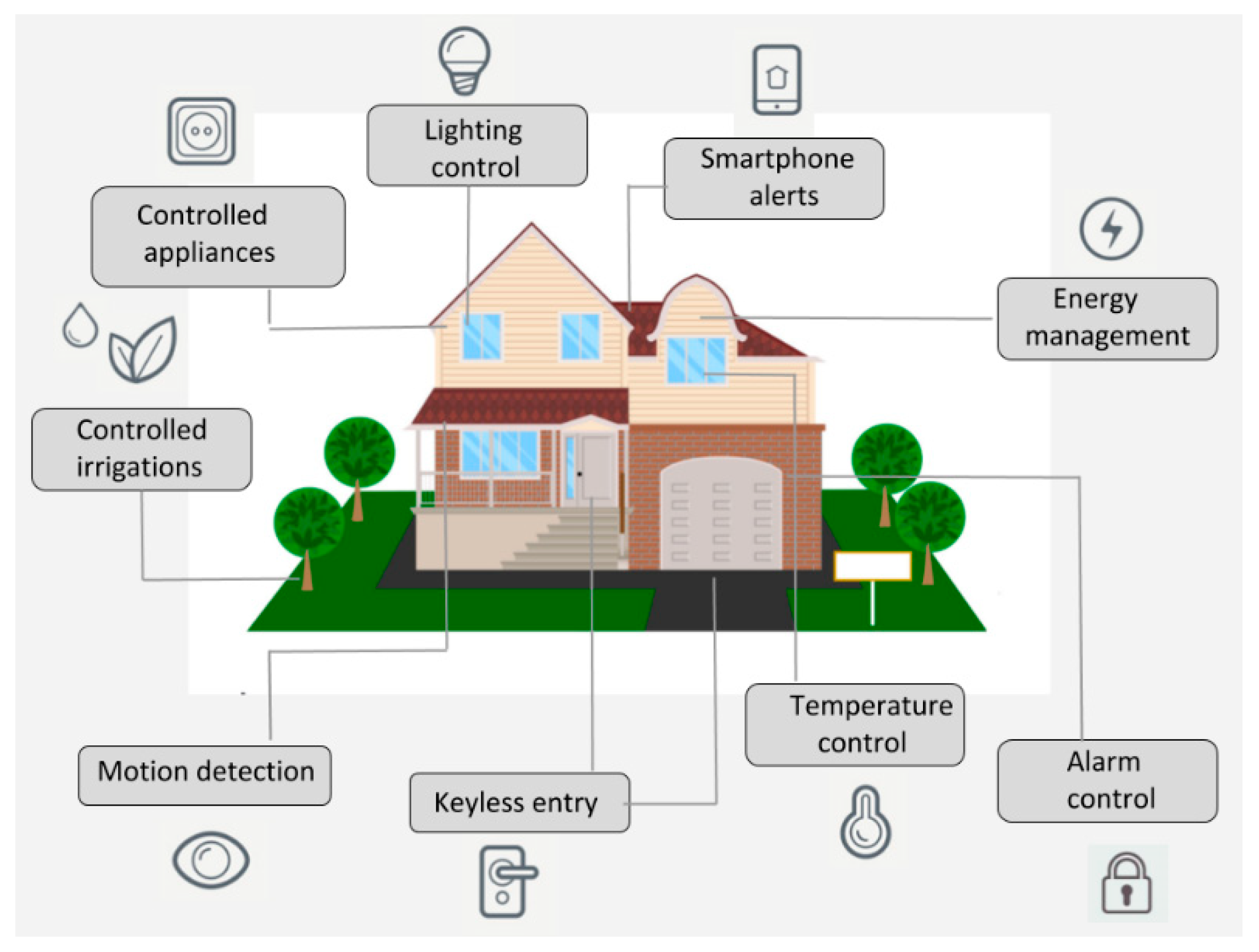
Smart Buildings: These are structures that use automated processes to control building operations such as heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), lighting, security, and other systems. The core objective is to improve building performance, enhance occupant well-being, and reduce operational costs.
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT refers to the network of interconnected devices that communicate and share data with each other. In the context of smart buildings, IoT devices include sensors, actuators, and control systems that collect and analyze data to optimize building functions.
Key Components:
- Sensors and Actuators: Devices that detect and respond to changes in the environment, such as temperature, humidity, light levels, and occupancy.
- Building Management Systems (BMS): Centralized platforms that monitor and control various building systems, integrating data from IoT devices.
- Data Analytics: Advanced software that analyzes data from IoT devices to provide insights and enable predictive maintenance and optimization.
Benefits of Smart Buildings and IoT
Energy Efficiency
One of the primary benefits of smart buildings is enhanced energy efficiency. By using IoT devices to monitor and control energy usage, smart buildings can significantly reduce energy consumption and lower utility costs.
Examples:
- Smart HVAC Systems: IoT sensors monitor indoor and outdoor temperatures, adjusting HVAC settings to optimize energy use.
- Automated Lighting: Smart lighting systems adjust brightness based on occupancy and natural light levels, reducing unnecessary energy consumption.
Improved Occupant Comfort and Productivity
Smart buildings prioritize occupant comfort and productivity by maintaining optimal indoor conditions and providing personalized environments. This can lead to higher satisfaction and productivity levels among occupants.
Examples:
- Personalized Climate Control: Occupants can use mobile apps to adjust temperature and lighting in their individual spaces, creating a customized environment.
- Indoor Air Quality Monitoring: IoT sensors monitor air quality parameters such as CO2 levels, adjusting ventilation to ensure a healthy indoor environment.
Enhanced Safety and Security
Smart buildings integrate advanced security systems that leverage IoT technology to enhance safety and security. These systems provide real-time monitoring, access control, and automated responses to potential threats.
Examples:
- Surveillance Systems: IoT-enabled cameras and sensors provide real-time video monitoring and analytics to detect suspicious activities.
- Access Control: Smart access control systems use biometric authentication and IoT devices to manage entry to restricted areas.
Predictive Maintenance and Reduced Downtime
IoT technology enables predictive maintenance by continuously monitoring the performance of building systems and identifying potential issues before they become critical. This reduces downtime and maintenance costs.
Examples:
- Equipment Monitoring: IoT sensors track the performance of HVAC systems, elevators, and other critical equipment, alerting maintenance teams to potential problems.
- Predictive Analytics: Data analytics software analyzes trends and patterns in equipment performance, predicting when maintenance is needed.
Key Features of Smart Buildings
Integrated Building Management Systems (BMS)
A Building Management System (BMS) is the backbone of a smart building, integrating various building systems into a single platform. This allows for centralized monitoring and control, improving operational efficiency.
Features:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of building systems, providing real-time data on performance and energy usage.
- Automated Controls: Automated adjustments to HVAC, lighting, and other systems based on occupancy, weather conditions, and other factors.
- Data Analytics: Advanced analytics tools that provide insights into building performance and identify opportunities for optimization.
IoT-Enabled Sensors and Devices
IoT sensors and devices are essential components of smart buildings, providing the data needed to monitor and control building systems. These devices can be installed throughout the building to collect information on various parameters.
Types of Sensors:
- Temperature and Humidity Sensors: Monitor indoor climate conditions and adjust HVAC settings accordingly.
- Occupancy Sensors: Detect the presence of occupants in a space, optimizing lighting and climate control.
- Air Quality Sensors: Measure air quality parameters such as CO2, VOCs, and particulate matter, ensuring a healthy indoor environment.
Smart Lighting Systems
Smart lighting systems use IoT technology to optimize lighting based on occupancy, natural light levels, and other factors. These systems improve energy efficiency and enhance occupant comfort.
Features:
- Automated Dimming: Adjusts lighting levels based on occupancy and available daylight.
- Remote Control: Allows occupants to control lighting using mobile apps or voice commands.
- Energy Monitoring: Tracks energy consumption and identifies opportunities for savings.
Advanced Security Systems
Smart buildings incorporate advanced security systems that leverage IoT technology to enhance safety and security. These systems provide real-time monitoring, access control, and automated responses to potential threats.
Features:
- Surveillance Cameras: IoT-enabled cameras provide real-time video monitoring and analytics to detect suspicious activities.
- Access Control: Smart access control systems use biometric authentication and IoT devices to manage entry to restricted areas.
- Alarm Systems: Automated alarms and notifications in response to security breaches or emergencies.
Notable Examples of Smart Buildings
The Edge, Amsterdam, Netherlands
The Edge is often cited as one of the world’s smartest and most sustainable office buildings. It uses a combination of IoT technology, renewable energy, and advanced building systems to optimize performance and enhance occupant comfort.
Key Features:
- IoT Sensors: Thousands of IoT sensors monitor lighting, temperature, and occupancy, adjusting systems in real-time.
- Energy Efficiency: The building generates more energy than it consumes, thanks to solar panels and other renewable energy sources.
- Personalized Workspaces: Occupants use a mobile app to find available workspaces and adjust their environment to their preferences.
Capital Tower, Singapore
Capital Tower is a prime example of how smart building technology can enhance energy efficiency and occupant comfort in a high-rise office building. The building integrates IoT sensors, advanced analytics, and automated systems to optimize performance.
Key Features:
- Smart HVAC System: IoT sensors monitor indoor climate conditions, adjusting HVAC settings to optimize energy use and comfort.
- Energy Management: Advanced analytics tools track energy consumption and identify opportunities for savings.
- Indoor Air Quality Monitoring: IoT sensors measure air quality parameters, ensuring a healthy indoor environment.
Torre Reforma, Mexico City, Mexico
Torre Reforma is a state-of-the-art skyscraper that incorporates smart building technology to enhance sustainability, safety, and occupant comfort. The building uses IoT devices and advanced systems to optimize performance and reduce environmental impact.
Key Features:
- Seismic Resilience: The building is designed to withstand earthquakes, with IoT sensors monitoring structural integrity in real-time.
- Energy Efficiency: IoT sensors and automated systems optimize energy use, reducing consumption and costs.
- Smart Lighting: Automated lighting systems adjust brightness based on occupancy and natural light levels.
Challenges and Considerations
Cybersecurity
The integration of IoT devices in smart buildings raises significant cybersecurity concerns. Protecting sensitive data and ensuring the security of building systems is critical to preventing cyber-attacks and maintaining occupant safety.
Challenges:
- Data Privacy: Ensuring that personal data collected by IoT devices is protected and used responsibly.
- System Vulnerabilities: Addressing potential vulnerabilities in IoT devices and networks to prevent unauthorized access.
Cost and Implementation
The initial cost of implementing smart building technology can be a barrier for some projects. However, the long-term benefits in terms of energy savings, reduced maintenance costs, and enhanced occupant comfort often justify the investment.
Challenges:
- Upfront Costs: Balancing the initial investment with the long-term savings and benefits of smart building technology.
- Integration: Ensuring that new smart systems are compatible with existing building infrastructure and systems.
Regulatory and Policy Support
The adoption of smart building technology requires supportive policies and regulations. Building codes and standards must evolve to incorporate smart building principles and incentivize sustainable practices.
Challenges:
- Regulatory Framework: Developing and implementing building codes that support the adoption of smart building technology.
- Incentives: Providing financial incentives and support for projects that implement smart building technology.
Future Trends in Smart Buildings and IoT
Integration with Smart Cities
As urban areas become more interconnected, smart buildings will play a crucial role in the development of smart cities. Integration with city-wide systems for energy, transportation, and communication will enhance the efficiency and sustainability of urban environments.
Trend:
- Smart City Integration: Smart buildings connected to city-wide IoT networks, sharing data and resources to optimize urban systems.
AI and Machine Learning
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) with IoT technology will enable more advanced and adaptive building systems. AI and ML can analyze vast amounts of data to predict trends, optimize performance, and enhance occupant experience.
Trend:
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms that predict equipment failures and schedule maintenance to prevent downtime.
- Adaptive Systems: Building systems that learn from occupant behavior and environmental conditions to continuously optimize performance.
Focus on Sustainability
Sustainability will remain a key focusin the evolution of smart buildings and IoT. Integrating renewable energy sources, optimizing resource use, and minimizing environmental impact will drive future developments.
Trend:
- Renewable Energy Integration: Smart buildings increasingly incorporate solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable energy sources to reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
- Water Conservation: IoT-enabled systems that monitor and manage water use, promoting efficient consumption and recycling.
- Zero-Carbon Buildings: The development of buildings designed to have net-zero carbon emissions, utilizing advanced technologies and sustainable practices.
Health and Well-being
The focus on health and well-being will shape the design of smart buildings, especially in the context of the post-pandemic world. Enhancing indoor air quality, promoting physical activity, and supporting mental health will be key priorities.
Trend:
- Health Monitoring: IoT sensors that monitor air quality, humidity, and other factors to maintain a healthy indoor environment.
- Biophilic Design: Incorporating natural elements and green spaces within buildings to improve occupant well-being.
- Touchless Technology: Reducing the need for physical contact with surfaces through voice-activated systems and motion sensors.
Flexible and Adaptive Spaces
The growing demand for flexible and adaptive spaces will influence smart building design. Buildings will be designed to easily accommodate changing needs, from reconfigurable office layouts to adaptable residential units.
Trend:
- Modular Design: Using modular components that can be easily reconfigured to create different spaces.
- Flexible Workspaces: Designing office buildings with adaptable layouts that support various work styles and activities.
- Smart Furniture: Furniture equipped with IoT technology to support flexible and dynamic use of space.
Conclusion
The evolution of smart buildings and IoT is transforming the architecture and construction industry, creating more efficient, sustainable, and comfortable built environments. By integrating advanced technologies and data-driven insights, smart buildings can optimize energy use, enhance occupant well-being, and improve overall building performance. As we move forward, the continued development of smart building technologies, supported by regulatory frameworks and industry collaboration, will play a crucial role in shaping the future of urban living. Embracing these innovations will enable us to create resilient, adaptive, and sustainable buildings that meet the challenges of the 21st century.