Introduction
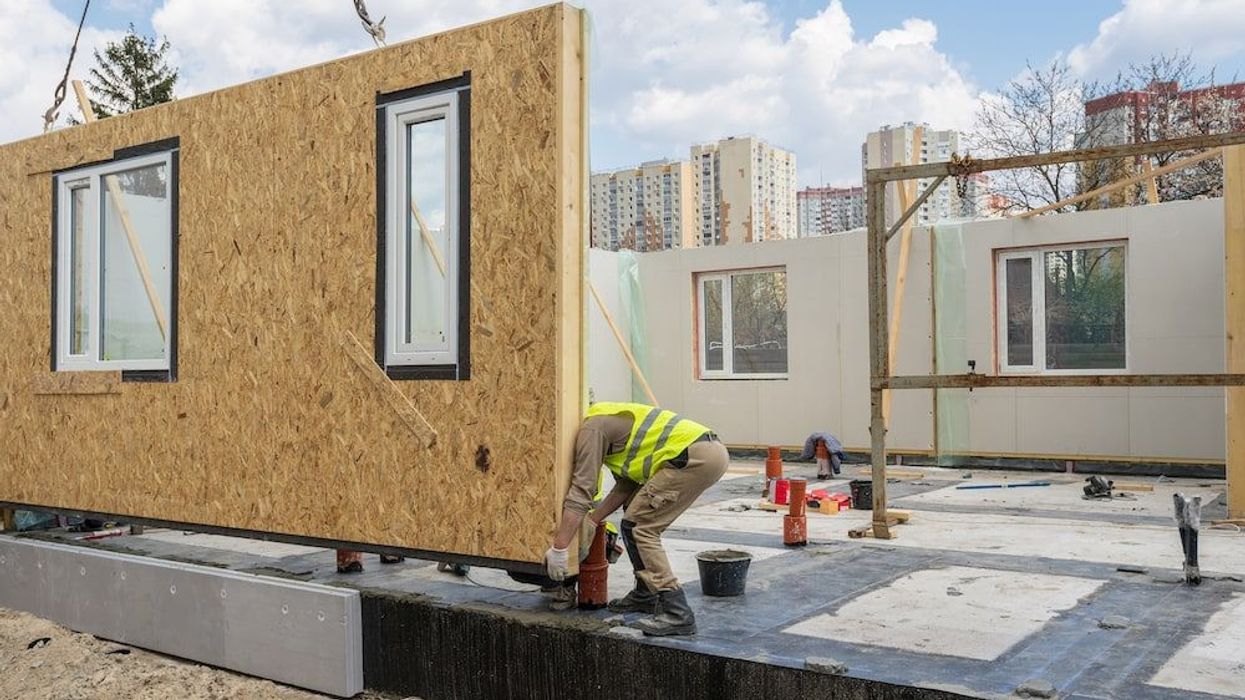
In the quest for efficiency, sustainability, and affordability in the construction industry, prefab and modular architecture have emerged as transformative solutions. Prefabricated (prefab) and modular construction methods involve assembling building components in a factory setting before transporting and installing them on-site. This approach not only reduces construction time and costs but also enhances quality control and minimizes environmental impact. As we move through 2022, innovations in prefab and modular architecture are reshaping the industry, offering new possibilities for residential, commercial, and public buildings. This article explores the latest advancements, benefits, and notable projects in prefab and modular architecture, highlighting their growing significance in modern construction.
Understanding Prefab and Modular Architecture
Definitions and Distinctions
Prefabrication refers to the process of manufacturing building components in a controlled factory environment. These components can range from simple structural elements to entire building modules.
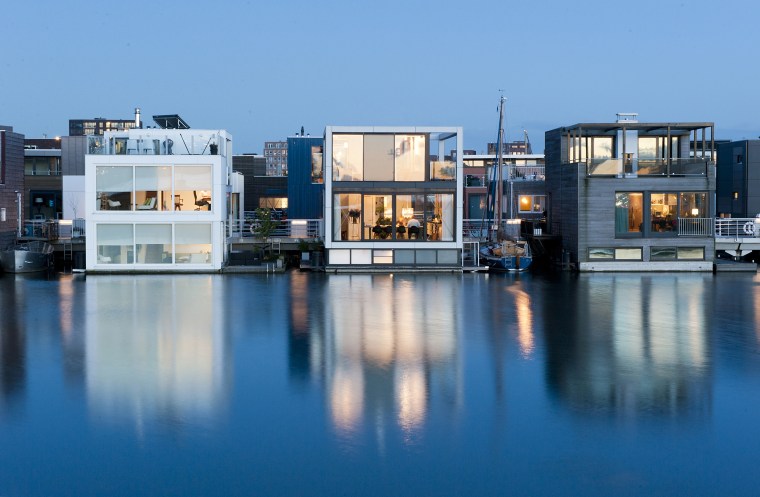
Modular construction is a subset of prefabrication that involves creating complete sections or modules of a building, which are then transported to the construction site and assembled. Each module is a fully finished unit, complete with interior and exterior finishes, fixtures, and systems.
Difference: While all modular construction is prefabricated, not all prefabrication is modular. Prefabrication can involve components like walls, floors, and roof trusses, whereas modular construction involves entire sections or rooms of a building.
Innovations in Prefab and Modular Architecture
Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
Recent advancements in manufacturing technologies have significantly enhanced the precision, efficiency, and scalability of prefab and modular construction. Technologies such as computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), and robotics are revolutionizing the production process.
Example:
- Automated robotic systems are used to assemble complex building components with high precision, reducing errors and labor costs.
Sustainable Materials and Practices
Sustainability is a key driver of innovation in prefab and modular architecture. The use of eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient systems, and sustainable manufacturing practices is becoming increasingly prevalent.
Example:
- Cross-laminated timber (CLT), a sustainable alternative to traditional construction materials, is gaining popularity in modular construction for its strength, versatility, and low environmental impact.
Digital Twin and Building Information Modeling (BIM)
Digital twin technology and Building Information Modeling (BIM) are transforming the design, planning, and management of prefab and modular projects. These technologies enable detailed virtual representations of buildings, facilitating accurate design, clash detection, and project coordination.
Example:
- BIM allows architects, engineers, and contractors to collaborate in a virtual environment, optimizing the design and construction process and reducing the risk of costly errors and delays.
3D Printing
3D printing is making inroads into prefab and modular construction, offering new possibilities for custom-designed components and rapid prototyping. This technology enables the creation of complex, bespoke elements that would be difficult or costly to produce using traditional methods.
Example:
- 3D-printed concrete panels and structural components are being used in modular construction, offering enhanced design flexibility and reduced material waste.
Benefits of Prefab and Modular Architecture
Reduced Construction Time
One of the most significant advantages of prefab and modular construction is the substantial reduction in construction time. Since components are manufactured off-site in parallel with site preparation, the overall project timeline is shortened.
Example:
- A modular hotel can be constructed in a fraction of the time required for traditional construction, with modules built and finished off-site while foundation work is underway on-site.
Cost Efficiency
Prefab and modular construction can lead to significant cost savings through economies of scale, reduced labor costs, and minimized material waste. The controlled factory environment also enhances quality control, reducing the likelihood of costly rework.
Example:
- Modular housing projects can achieve cost savings of up to 20% compared to traditional construction methods, making affordable housing more feasible.
Enhanced Quality and Consistency
The controlled factory setting of prefab and modular construction ensures consistent quality and precision. Components are manufactured to exact specifications, reducing variability and ensuring a higher standard of construction.
Example:
- Hospital modules built in a factory setting can meet stringent healthcare standards, ensuring high-quality, sterile environments for patient care.
Sustainability and Reduced Environmental Impact
Prefab and modular construction contribute to sustainability by reducing material waste, lowering energy consumption, and minimizing the environmental impact of construction activities. The use of sustainable materials and energy-efficient systems further enhances the environmental benefits.
Example:
- Modular buildings designed with energy-efficient systems and renewable energy sources can achieve net-zero energy consumption, reducing their carbon footprint.
Notable Projects in Prefab and Modular Architecture
B2 Tower, New York City, USA
The B2 Tower, also known as 461 Dean, is a landmark modular building in Brooklyn, New York. Completed in 2016, the 32-story residential tower was constructed using modular units fabricated off-site. The project demonstrated the potential of modular construction for high-rise buildings.
Key Features:
- 930 modular units were manufactured in a factory and assembled on-site.
- The project reduced construction time by approximately 20% compared to traditional methods.
- High-quality, energy-efficient units with modern amenities.
The Yard, London, UK
The Yard is a modular housing development in London, offering affordable and sustainable living spaces. The project utilizes prefabricated modules to create modern, energy-efficient homes that meet high environmental standards.
Key Features:
- Use of cross-laminated timber (CLT) for sustainable construction.
- Rapid assembly of modular units, reducing construction time and disruption.
- Energy-efficient design with renewable energy systems.
Clement Canopy, Singapore
Clement Canopy is a 40-story residential project in Singapore that employed modular construction techniques. The project set a new benchmark for high-rise modular construction in the region, showcasing the potential for large-scale prefab solutions.
Key Features:
- Use of precast concrete modules for rapid construction.
- High-quality finishes and modern amenities in each unit.
- Significant reduction in on-site labor and construction waste.
Challenges and Considerations
Design and Customization Limitations
While prefab and modular construction offer many benefits, they can also impose limitations on design flexibility and customization. Standardized modules may not always accommodate unique architectural features or complex designs.
Challenge:
- Balancing the efficiency of modular construction with the need for bespoke design solutions.
Transportation and Logistics
Transporting prefabricated modules from the factory to the construction site can present logistical challenges, particularly for large or complex modules. Ensuring the safe and efficient delivery of these components is critical to project success.
Challenge:
- Managing transportation logistics to minimize delays and damage to modules during transit.
Regulatory and Permitting Hurdles
Navigating the regulatory landscape for prefab and modular construction can be complex. Building codes and permitting processes may need to be adapted to accommodate these innovative construction methods.
Challenge:
- Ensuring compliance with local building codes and securing necessary permits for modular construction projects.
Future Trends in Prefab and Modular Architecture
Increased Adoption of Smart Technologies
The integration of smart technologies, such as IoT, AI, and advanced sensors, will enhance the functionality and efficiency of modular buildings. These technologies can improve energy management, occupant comfort, and building maintenance.
Trend:
- Smart modular buildings equipped with advanced energy management systems and automated controls.
Expansion of Modular Construction to New Sectors
While modular construction has traditionally been associated with residential and commercial buildings, it is expanding into new sectors such as healthcare, education, and hospitality. The versatility and efficiency of modular construction make it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Trend:
- Growth in modular hospitals, schools, and hotels, driven by the need for rapid deployment and high-quality construction.
Emphasis on Circular Economy Principles
The adoption of circular economy principles, which prioritize resource efficiency and waste reduction, will drive innovation in prefab and modular construction. Designing for disassembly and reuse will become increasingly important.
Trend:
- Modular buildings designed with reusable components and materials, contributing to a circular construction economy.
Conclusion
Innovations in prefab and modular architecture are revolutionizing the construction industry, offering efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective solutions for a wide range of building projects. Advanced manufacturing technologies, sustainable materials, and digital tools are driving the evolution of these construction methods, enhancing their appeal and feasibility. As we navigate through 2022, the continued growth and development of prefab and modular architecture will play a crucial role in addressing the challenges of urbanization, affordability, and environmental sustainability. By embracing these innovative approaches, architects and developers can create high-quality, resilient, and future-ready buildings that meet the needs of modern society.