Introduction roduction
In recent years, the architecture and construction industries have been undergoing a digital revolution, propelled by advancements in technology that are reshaping traditional practices and approaches. One of the most transformative innovations to emerge is the concept of digital twins. Initially popularized in manufacturing and industrial sectors, digital twins are now making significant inroads into architecture, promising to revolutionize how buildings are designed, constructed, and maintained.
Understanding Digital Twins
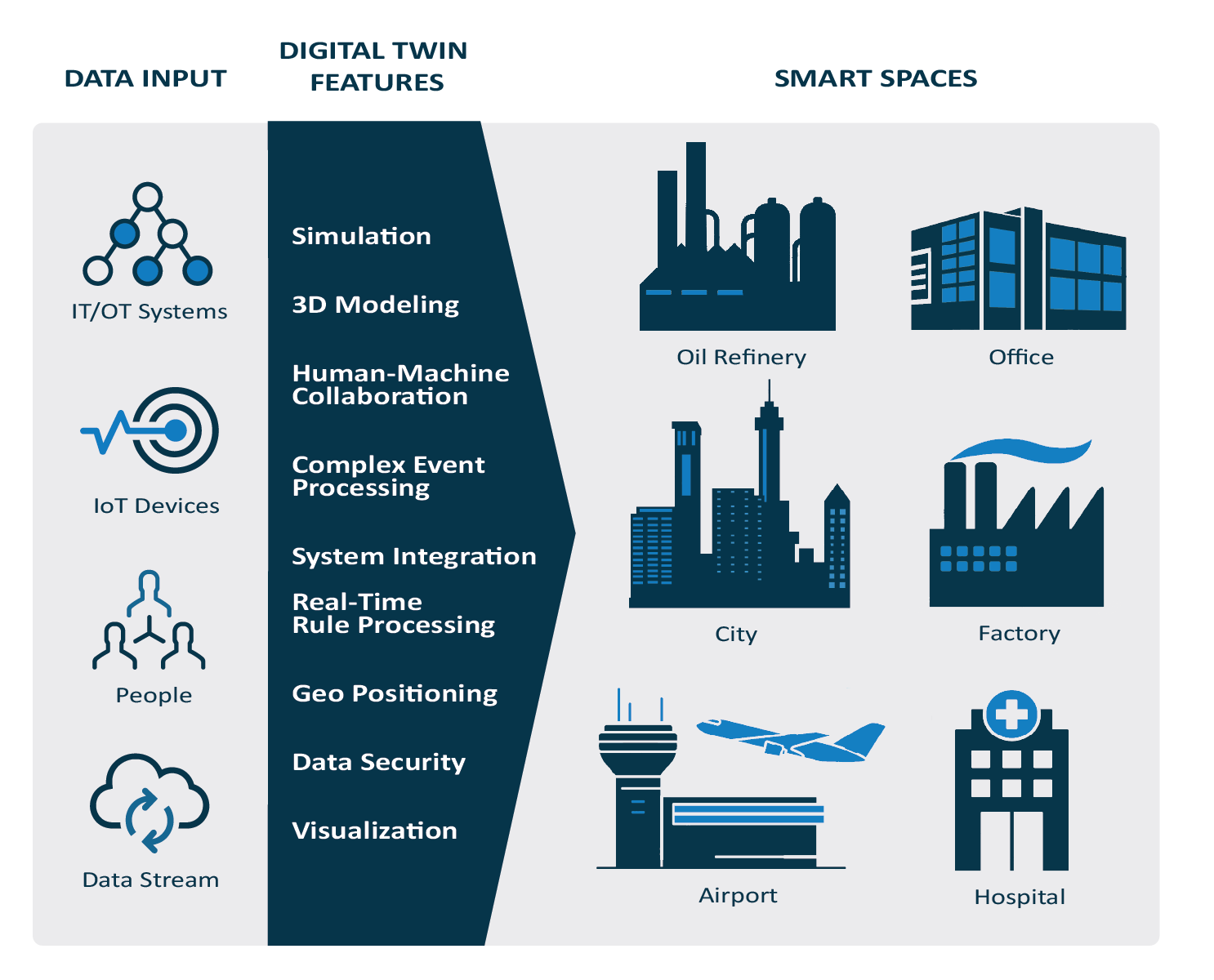
At its core, a digital twin is a virtual replica or simulation of a physical entity or system. In the context of architecture, a digital twin represents a building or infrastructure project in its entirety, including its structural elements, systems, and even environmental conditions. This virtual model is not static but dynamic, continuously updated with real-time data from sensors embedded throughout the building.
The concept of digital twins goes beyond simple 3D models used in architectural design. It integrates data from various sources, such as Building Information Modeling (BIM), Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, and other monitoring devices. This integration allows architects, engineers, and building managers to gain unprecedented insights into how a building functions throughout its lifecycle.
Applications of Digital Twins in Architecture
1. Design and Simulation
Digital twins enable architects to create highly detailed and accurate simulations of buildings before they are constructed. By leveraging advanced modeling techniques and real-world data, architects can visualize how different design choices will impact a building’s performance, energy efficiency, and occupant comfort. This predictive capability helps in optimizing designs for better functionality and sustainability.
2. Construction and Project Management
During the construction phase, digital twins facilitate better project management and coordination. By providing real-time updates on construction progress and resource allocation, stakeholders can identify and address issues promptly, thereby minimizing delays and cost overruns. Virtual simulations also aid in safety planning and risk management by identifying potential hazards before they manifest on-site.
3. Monitoring and Maintenance
Once a building is operational, digital twins continue to play a crucial role in its ongoing management and maintenance. IoT sensors embedded within the building collect data on various parameters such as temperature, humidity, energy consumption, and structural integrity. This data is fed into the digital twin, allowing for continuous monitoring of building performance and early detection of maintenance issues.
Benefits of Digital Twins in Architecture
1. Improved Efficiency and Cost Savings
Digital twins streamline the design and construction process, leading to reduced material wastage, fewer errors, and optimized resource utilization. By identifying inefficiencies early on, architects can make informed decisions that contribute to overall project cost savings and improved profitability.
2. Enhanced Sustainability
Sustainability is a critical consideration in modern architecture. Digital twins enable architects to assess the environmental impact of design choices and operational practices. By analyzing energy consumption patterns and environmental conditions, architects can optimize building performance to minimize carbon footprint and achieve green building certifications.
3. Real-Time Decision Making
The real-time data provided by digital twins empowers stakeholders to make data-driven decisions swiftly. Whether it’s adjusting building systems for optimal performance or responding to maintenance needs proactively, architects and building managers can act promptly to ensure the building operates efficiently and meets occupant needs.
Case Studies and Examples
Case Study 1: The Edge, Amsterdam
One notable example of digital twin implementation is “The Edge” in Amsterdam, often touted as the world’s most sustainable office building. Digital twins monitor everything from energy usage to occupancy patterns, allowing for precise adjustments that enhance efficiency and user comfort.
Case Study 2: Smart Cities Initiatives
In the realm of urban planning, digital twins are being used to simulate entire cityscapes. Cities like Singapore and Barcelona use digital twins to model infrastructure, optimize traffic flow, and improve public services, demonstrating the scalability and versatility of this technology beyond individual buildings.
Challenges and Considerations
While the potential benefits of digital twins in architecture are substantial, several challenges must be addressed for widespread adoption:
- Data Integration and Interoperability: Ensuring compatibility and seamless integration of data from diverse sources.
- Privacy and Security Concerns: Safeguarding sensitive data collected by IoT sensors and digital twin platforms.
- Cost and Complexity: Initial investment in technology and expertise required for developing and maintaining digital twins.
Future Directions
Looking ahead, the evolution of digital twins in architecture promises even greater advancements. As technology continues to mature, we can expect enhanced AI-driven analytics, augmented reality interfaces for immersive experiences, and further integration with smart building technologies. These developments will undoubtedly redefine how architects, engineers, and stakeholders collaborate and innovate in the built environment.
Conclusion
Digital twins represent a paradigm shift in architecture, offering a holistic approach to building design, construction, and management. By harnessing the power of data and advanced simulation techniques, architects can create more sustainable, efficient, and responsive buildings. As the technology matures and becomes more accessible, digital twins are set to become an indispensable tool in shaping the cities and structures of tomorrow.
In essence, digital twins in architecture are not merely virtual replicas but transformative platforms that empower architects to design smarter, build efficiently, and manage effectively in an increasingly complex and interconnected world.